
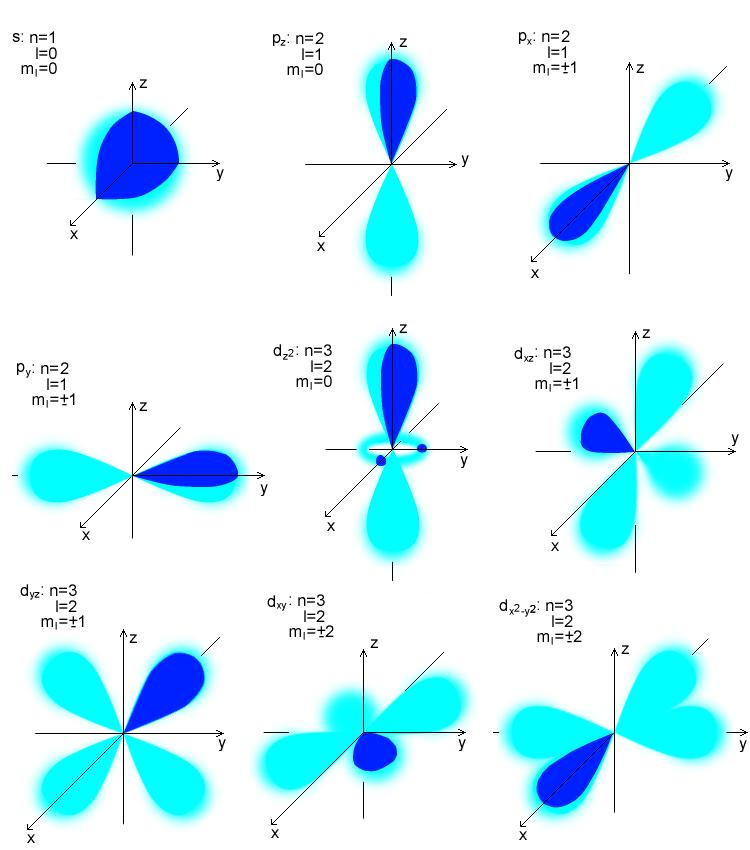
The plots of Ψ2 in x, y and z axes show these probabilities, and they take the shape of s, p, d and f orbitals. On the contrary, if the Ψ2 is low, then the electron probability density is low.

Therefore, in the space, electron probability density is large. So, if Ψ2 is a large value, then the probability of finding the electron in that space is higher. According to Born, Ψ2 expresses the probability of finding an electron in a particular location. Max Born points out a physical meaning to the square of wave function (Ψ2), after Schrodinger put forward his theory. However, molecular orbitals can change their shapes depending on the hybridisation they are in. Atomic orbitals s,p,d and f have fixed shapes. Atomic orbitals are named s, p, d, f and molecular orbitals are classified as bonding and antibonding. Atomic orbitals depict the location where the electron can probably be found in the atom where as molecular orbitals describe the probable location in a molecule as a whole. So, atomic orbitals join together to form molecular ones. We then have a molecular orbital.Īctually, we can get two molecular orbitals, because the electrons behave as waves.īut the main point is, a molecular orbital extends over more than one atom.Ītomic orbitals are found in atoms and molecular in molecules. When two H atoms get close enough, their orbitals merge to include both nuclei. The simplest atomic orbital is the spherical 1s orbital of hydrogen.
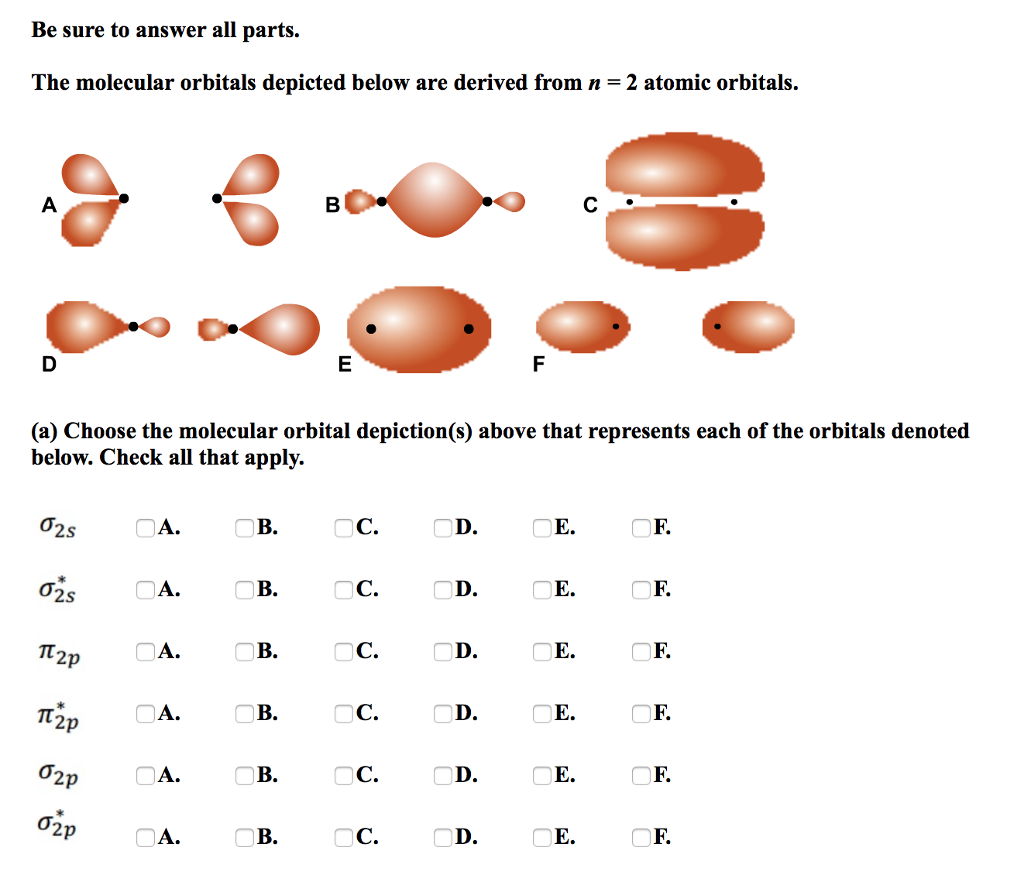
A molecular orbital extends over more than one atom.Īn orbital is a region in space where an electron is most likely to be found.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
